Forced Oscillations
Forced Oscillations: Overview
This Topic covers sub-topics such as Forced Oscillations, Free Oscillations, Driving Frequency, Natural Frequency of a System and, Behaviour of Forced Oscillation When Driving Frequency is Far from Natural Frequency
Important Questions on Forced Oscillations
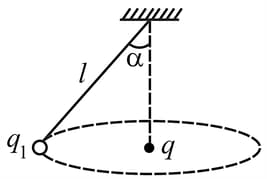
A charged ball of positive charge is revolving around another positive charge as shown in a conical pendulum. The motion is in a horizontal plane :-
When the ratio of natural frequency and driving frequency becomes unity, _____ occurs.
Free oscillation is also called as free _____.
The frequency of free oscillation called _____ frequency.
In a free oscillation,what happens to the amplitude,frequency and energy of the oscillating body?
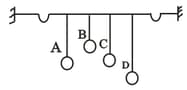
In the given arrangement which pair can represents the resonance.(All are simple pendulum).
The variation of amplitude of forced oscillation vs driving frequency. Which part represents least damping.
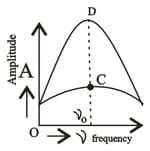
The variation of amplitude of forced oscillation vs driving frequency, which point represents the heavy damping.
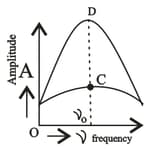
What is the frequency with which forced periodic oscillations oscillate?
A vibrating system is analysed, and it is found that two successive oscillations have amplitudes of and respectively. The damping ratio of the system is:
A mechanical system is oscillating at resonance with a constant amplitude. Which one of the following statements is not correct?
In case of a forced oscillation, the resonance peak becomes very sharp when the
The vibrations that can continue even after the external force is removed are called free vibrations or natural vibrations.
Natural frequency of a body depends on the shape, size, and _____ (elasticity/intensity) of the body.
In case of a forced vibration, the resonance wave becomes very sharp when the
Which of the diagrams shown in figure represents variation of total mechanical energy of a pendulum oscillating in water as function of time?
When a body of natural frequency is subjected to the external force vibrating with frequency , the body vibrates with frequency under steady state with an amplitude which depends upon
A metal wire of linear mass density of is stretched with a tension of kg-wt between two rigid supports 1 m apart. The wire passes at its middle point between the poles of a permanent magnet and it vibrates in resonance when carrying an alternating current of frequency n. the frequency n of the alternating sources is
A particle, with restoring force proportional to displacement and resisting force proportional to velocity is subjected to a force.
If the amplitude of the particle is maximum for and the energy of the particle is maximum for then
